Knowing how to understand the Electromagnetic Spectrum

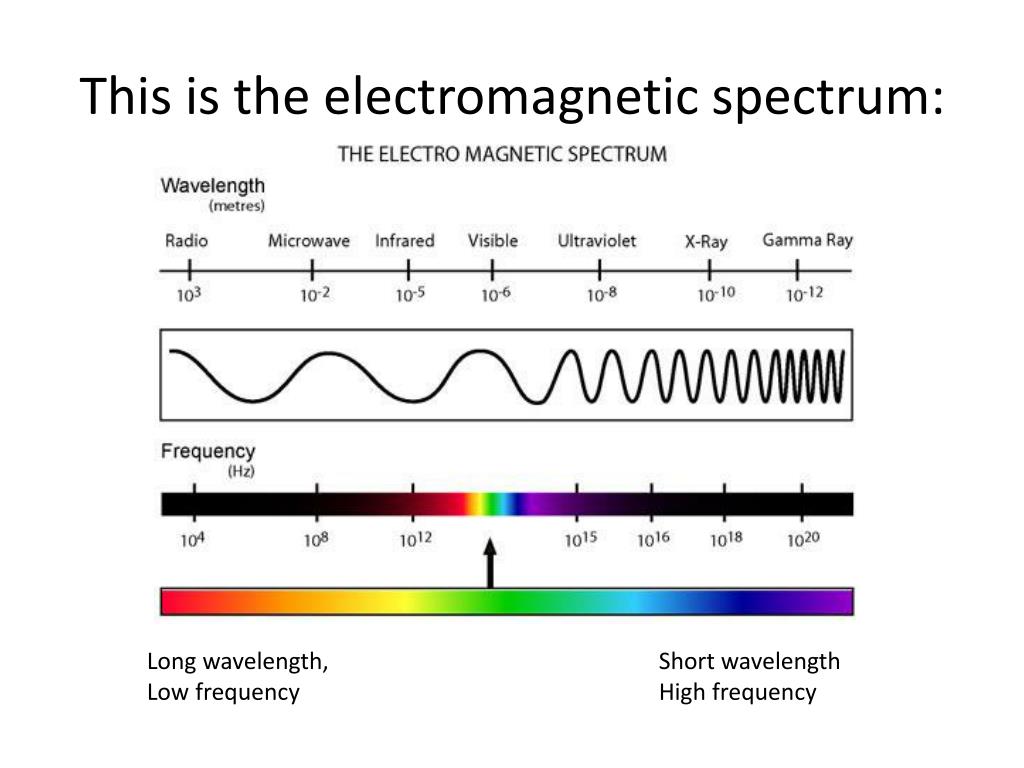
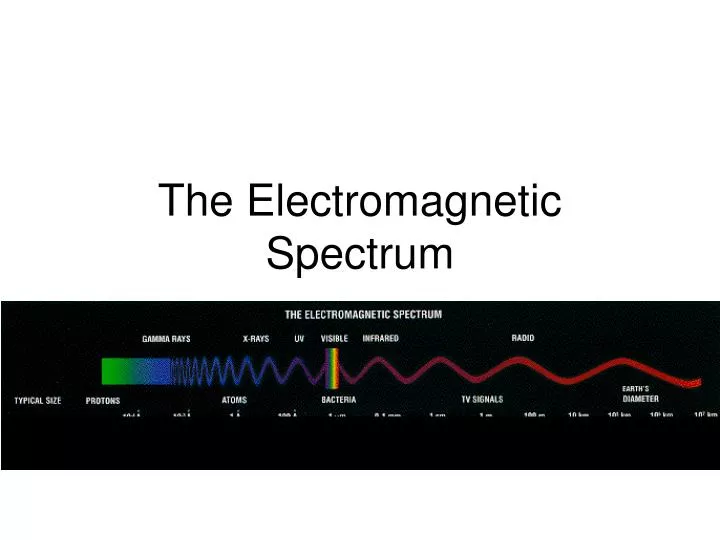
The electromagnetic spectrum is the spectrum of electromagnetic waves that range from visible light to gamma rays. This is an important part of science and understanding the electromagnetic spectrum is important. In this article I am going to discuss some of the most important aspects of this range and the way they work.
Infrared
Infrared refers to the electromagnetic spectrum that extends past the red portion of the visible light spectrum. Infrared spectrum is utilized to determine the thermal properties of objects. It is also used in night equipment for night vision.
In general, infrared is classified into near infrared and infrared. Near infrared is the wavelength that contains the frequencies with the smallest frequencies. These wavelengths are in the range of one to five microns. There are two long and intermediate infrared bands. Each has their own distinct wavelengths.
The most well-known use for infrared is found in night vision goggles for soldiers. These glasses convert infrared light into the visible wavelengths for nighttime vision. However, infrared light can used in wireless and wired communication.
There is no known link between infrared and skin cancer. However, the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) has provided guidelines regarding the limits of exposure to incoherent visible and infrared radiation.
Visible light
Visible light is part in the spectrum known as electromagnetic. The Sun is our main lighting source. Other sources of visible light are the moon and stars. It is important to know that we can't see the infrared and ultraviolet wavelengths. But, we can see the red and blue light. These colors are mixed creating what we call white light.
There are many other obscure elements of the electromagnetic spectrum including radio waves and infrared. Some of these are employed in radio, television and mobile communications. The best method to utilize them is to design the appropriate kind of filter. In this way we can lessen the negative consequences of these elements to our bodies. Additionally, we can build a virtual environment where we can look at these components without the use of our eyes.
While the longest and the shortest wavelengths of the visible light may be the most visible however, the most efficient and pleasing to the eye are the shortwave infrared (SWIR) as well as microwave frequency.
UV
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a part in the spectrum known as electromagnetic. It is used to serve a variety of purposes. But it is also damaging. UVB and UVC radiation are not good for eyesight and can cause skin disease.
This type of energy is absorbed by molecules and start chemical reactions. The molecule that is absorbing it will emit visible light or emit fluorescence.
The ultraviolet spectrum is split into three main categories, which are the extreme, the near as well as the middle. Typical ultraviolet sources include arc lamps, lasers, and light-emitting diodes.
While the wavelengths of UV rays are shorter that those of X-rays, they possess more energy. This is useful for breaking the bonds between chemical compounds. These waves are often referred to by the name of nonionizing radiation.
In biochemistry, the UV spectrum is often used to determine the absorption of a particular substance. There are many types of substances that have significant absorption bands of light in the UV.
Ultraviolet light is a member of the electromagnetic spectrum, which is produced from the sun. Its spectrum is between 10 and 4100 nanometers. Its frequency ranges from 800 THz to 30 PHz. However, most people cannot be able to see it.
X-rays
X-rays are electromagnetic radiation with high energy. Unlike gamma rays and ultraviolet light, Xrays have wavelengths less than visible light and are able to penetrate thin objects. They are utilized in a variety types of applications in medicine, including imaging bones and tissue. Several types of X-rays exist.
Hard X-rays can be produced by the collision of an electron with an atom. This causes a hole inside the electron shell of an atom. Another electron could fill in the gap. Alternatively, the incoming electron might kick out an atom. In this case, some of the energy generated by the photon is transferred to the scattering electron.
A X-ray should not be mistaken for the X-band which is a low-energy spectrum in the electromagnetic spectrum. While the two bands are separated by only a couple of centimeters in size, they don't share the same features.
Since X-rays penetrate, they can be used in a myriad of ways. For example, X-rays are used in security screening processes to identify cracks in baggage. In addition, they are utilized in radiotherapy for cancer patients. The X-rays can also be used to discover the structural components of various materials like cement.
spectrum em waves rays
Gamma rays are the most high energy forms of electromagnetic radiation. In reality, all high energy photons are gamma rays. They are generated by nuclear decay and high-energy physics experiments. They are among the most energetic photons found in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Due to their powerful energy, gamma rays can be capable of reaching deep into materials. The possibility exists for gamma beam to penetrate up to several feet of lead.
Several high-energy physics experiments produce the gamma radiation. For instance the radiation of particles from relativity directed by the magnetic field of a hypernova can be detected at a distance of 10 , billion light years.
Some gamma rays are emitted by the nucleus of some radionuclides after they have gone through the process of radioactive decay. Other sources of gamma rays include atomic transformations, annihilation, and sub-atomic particle interactions.
The majority of gamma rays in astronomy come from different mechanisms. Gamma rays from supernovae and nuclear fallout are two of the most energetic types in electromagnetic radiation. This makes them an excellent source to explore the universe.
Certain gamma rays can cause harm to cells within the body. However, gamma rays aren't as powerful like beta and alpha rays, and therefore tend to be less likely to trigger cancer. Nevertheless, gamma rays can alter the DNA structure and may cause burns. Even the smallest amounts of gamma radiations could cause ionization in the body.
